เช่นเดียวกับรุ่นก่อนๆ Android 16 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้มีผลเฉพาะกับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ขึ้นไป หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ขึ้นไป คุณควรแก้ไขแอปให้รองรับลักษณะการทำงานเหล่านี้ในกรณีที่เกี่ยวข้อง
นอกจากนี้ โปรดตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่มีผลต่อแอปทั้งหมด
ที่ทำงานบน Android 16 ไม่ว่า targetSdkVersion ของแอปจะเป็นอย่างไร
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งมีจุดประสงค์ เพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกันและใช้งานง่ายยิ่งขึ้น
การเลือกไม่ใช้แบบไร้ขอบจะสิ้นสุดลง
Android 15 บังคับใช้การแสดงผลแบบขอบต่อขอบสำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API
ระดับ 35) แต่แอปของคุณสามารถเลือกไม่ใช้ได้โดยตั้งค่า
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement เป็น true สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) ระบบจะเลิกใช้งานและปิดใช้ R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement และแอปของคุณจะเลือกไม่ใช้การแสดงผลแบบไร้ขอบไม่ได้
- หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) และทำงานบนอุปกรณ์ Android 15
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementจะยังคงทำงานได้ - หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) และทำงานบนอุปกรณ์ Android 16 ระบบจะปิดใช้
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement
สำหรับการทดสอบใน Android 16 โปรดตรวจสอบว่าแอปของคุณรองรับการแสดงผลแบบขอบจรดขอบ และ
นำการใช้ R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement ออกเพื่อให้แอปของคุณ
รองรับการแสดงผลแบบขอบจรดขอบในอุปกรณ์ Android 15 ด้วย หากต้องการรองรับการแสดงผลแบบขอบจรดขอบ
โปรดดูคำแนะนำเกี่ยวกับ Compose และ Views
ต้องย้ายข้อมูลหรือเลือกไม่ใช้เพื่อใช้การคาดการณ์การย้อนกลับ
สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) ขึ้นไปและทำงานในอุปกรณ์ Android 16 ขึ้นไป ระบบจะเปิดใช้ภาพเคลื่อนไหวของระบบย้อนกลับแบบคาดการณ์ (ย้อนกลับไปหน้าแรก ข้ามงาน และข้ามกิจกรรม) โดยค่าเริ่มต้น
นอกจากนี้ ระบบจะไม่เรียกใช้ onBackPressed และจะไม่ส่ง KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK อีกต่อไป
หากแอปของคุณสกัดกั้นเหตุการณ์ย้อนกลับและคุณยังไม่ได้ย้ายข้อมูลไปยังการคาดการณ์
การย้อนกลับ ให้อัปเดตแอปเพื่อใช้ API การนำทางย้อนกลับที่รองรับ หรือ
เลือกไม่ใช้ชั่วคราวโดยตั้งค่าแอตทริบิวต์
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback เป็น false ในแท็ก
<application> หรือ <activity> ของไฟล์ AndroidManifest.xml ของแอป
เลิกใช้งานและปิดใช้ Elegant Font API
แอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) จะมีแอตทริบิวต์
elegantTextHeight
TextView ตั้งค่าเป็น true โดยค่าเริ่มต้น ซึ่งจะแทนที่แบบอักษรแบบย่อด้วยแบบอักษรที่อ่านง่ายกว่ามาก คุณลบล้างค่านี้ได้โดยตั้งค่าแอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight เป็น false
Android 16 จะเลิกใช้งานแอตทริบิวต์
elegantTextHeight
และระบบจะละเว้นแอตทริบิวต์เมื่อแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 เราจะเลิกใช้ "UI
fonts" ที่ควบคุมโดย API เหล่านี้ ดังนั้นคุณควรปรับเลย์เอาต์ใดๆ เพื่อให้การแสดงข้อความในภาษาอาหรับ ลาว เมียนมาร์ ทมิฬ คุชราต กันนาดา มาลายาลัม โอเดีย เตลูกู หรือไทยมีความสอดคล้องกันและพร้อมใช้งานในอนาคต
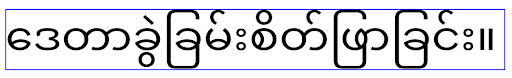 ลักษณะการทำงานของ
ลักษณะการทำงานของ elegantTextHeight สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android
14 (API ระดับ 34) และต่ำกว่า หรือสำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35)
ซึ่งลบล้างค่าเริ่มต้นโดยการตั้งค่าแอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight
เป็น false ลักษณะการทํางานของ
ลักษณะการทํางานของ elegantTextHeight สําหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android
16 (API ระดับ 36) หรือสําหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ที่ไม่ได้
ลบล้างค่าเริ่มต้นโดยการตั้งค่าแอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight
เป็น falseฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งจะแก้ไขหรือ ขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการจัดกำหนดเวลางานแบบอัตราคงที่
ก่อนที่จะกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 เมื่อ scheduleAtFixedRate พลาดการเรียกใช้งานเนื่องจากอยู่นอกวงจรการประมวลผลที่ถูกต้อง การเรียกใช้ทั้งหมดที่พลาดไปจะดำเนินการทันทีเมื่อแอปกลับไปยังวงจรการประมวลผลที่ถูกต้อง
เมื่อกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ระบบจะเรียกใช้scheduleAtFixedRate ที่พลาดไปไม่เกิน1 ครั้งทันทีเมื่อแอปกลับมาอยู่ในวงจรที่ถูกต้อง การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานนี้คาดว่าจะช่วยปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพของแอป ทดสอบลักษณะการทำงานนี้ในแอปเพื่อดูว่าแอปได้รับผลกระทบหรือไม่
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังทดสอบโดยใช้เฟรมเวิร์กความเข้ากันได้ของแอปและเปิดใช้ Flag STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat ได้ด้วย
รูปแบบของอุปกรณ์
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้สำหรับแอปเมื่อ แสดงบนอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
เลย์เอาต์แบบปรับขนาดได้
With Android apps now running on a variety of devices (such as phones, tablets, foldables, desktops, cars, and TVs) and windowing modes on large screens (such as split screen and desktop windowing), developers should build Android apps that adapt to any screen and window size, regardless of device orientation. Paradigms like restricting orientation and resizability are too restrictive in today's multidevice world.
Ignore orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions no longer apply on displays with smallest width >= 600dp. Apps fill the entire display window, regardless of aspect ratio or a user's preferred orientation, and pillarboxing isn't used.
This change introduces a new standard platform behavior. Android is moving toward a model where apps are expected to adapt to various orientations, display sizes, and aspect ratios. Restrictions like fixed orientation or limited resizability hinder app adaptability. Make your app adaptive to deliver the best possible user experience.
You can also test this behavior by using the
app compatibility framework and enabling the
UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat flag.
Common breaking changes
Ignoring orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions might impact your app's UI on some devices, especially elements that were designed for small layouts locked in portrait orientation: for example, issues like stretched layouts and off-screen animations and components. Any assumptions about aspect ratio or orientation can cause visual issues with your app. Learn more about how to avoid them and improve your app's adaptive behaviour.
Allowing device rotation results in more activity re-creation, which can result in losing user state if not properly preserved. Learn how to correctly save UI state in Save UI states.
Implementation details
The following manifest attributes and runtime APIs are ignored across large screen devices in full-screen and multi-window modes:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
The following values for screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), and
getRequestedOrientation() are ignored:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Regarding display resizability, android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio, and android:maxAspectRatio have no effect.
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), app orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio constraints are ignored on large screens by default, but every app that isn't fully ready can temporarily override this behavior by opting out (which results in the previous behavior of being placed in compatibility mode).
Exceptions
The Android 16 orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions don't apply in the following situations:
- Games (based on the
android:appCategoryflag) - Users explicitly opting in to the app's default behavior in aspect ratio settings of the device
- Screens that are smaller than
sw600dp
Opt out temporarily
To opt out a specific activity, declare the
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY manifest property:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
If too many parts of your app aren't ready for Android 16, you can opt out completely by applying the same property at the application level:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
สุขภาพและการออกกำลังกาย
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับข้อมูลสุขภาพ และการออกกำลังกาย
สิทธิ์ด้านสุขภาพและการออกกำลังกาย
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher,
BODY_SENSORS permissions use more granular permissions
under android.permissions.health, which Health Connect
also uses. As of Android 16, any API previously requiring BODY_SENSORS
or BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND requires the corresponding
android.permissions.health permission instead. This affects the following data
types, APIs, and foreground service types:
HEART_RATE_BPMfrom Health Services on Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEfrom Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyandheartRateBpmfromProtoLayouton Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHwhere the respectiveandroid.permission.healthpermission is needed in place ofBODY_SENSORS
If your app uses these APIs, it should request the respective granular permissions:
- For while-in-use monitoring of Heart Rate, SpO2, or Skin Temperature:
request the granular permission under
android.permissions.health, such asREAD_HEART_RATEinstead ofBODY_SENSORS. - For background sensor access: request
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDinstead ofBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
These permissions are the same as those that guard access to reading data from Health Connect, the Android datastore for health, fitness, and wellness data.
Mobile apps
Mobile apps migrating to use the READ_HEART_RATE and other granular
permissions must also declare an activity to display
the app's privacy policy. This is the same requirement as Health Connect.
การเชื่อมต่อ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ในสแต็กบลูทูธ เพื่อปรับปรุงการเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ต่อพ่วง
เจตนาใหม่ในการจัดการการสูญเสียพันธะและการเปลี่ยนแปลงการเข้ารหัส
การจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงที่ดีขึ้นทำให้ Android 16 เปิดตัว Intent ใหม่ 2 รายการเพื่อให้แอปรับรู้ถึงการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงและการเปลี่ยนแปลงการเข้ารหัสได้ดียิ่งขึ้น
ตอนนี้แอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ทําสิ่งต่อไปนี้ได้
- รับ Intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGเมื่อตรวจพบการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงระยะไกล ซึ่งช่วยให้สามารถแสดงความคิดเห็นที่เป็นประโยชน์ต่อผู้ใช้มากขึ้นและดำเนินการที่เหมาะสม - รับ Intent
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEเมื่อใดก็ตามที่สถานะการเข้ารหัสของลิงก์มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง ซึ่งรวมถึงการเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะการเข้ารหัส การเปลี่ยนแปลงอัลกอริทึมการเข้ารหัส และการเปลี่ยนแปลงขนาดคีย์การเข้ารหัส แอปต้องถือว่าการเชื่อมโยงได้รับการคืนค่าหากลิงก์ได้รับการเข้ารหัสเรียบร้อยแล้วเมื่อได้รับ IntentACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEในภายหลัง
การปรับให้เข้ากับการใช้งาน OEM ที่หลากหลาย
แม้ว่า Android 16 จะเปิดตัว Intent ใหม่เหล่านี้ แต่การใช้งานและการออกอากาศอาจแตกต่างกันไปตามผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ (OEM) แต่ละราย นักพัฒนาแอปควรออกแบบการจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงให้ปรับให้เข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่อาจเกิดขึ้นเหล่านี้ได้อย่างราบรื่น เพื่อให้แอปมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่สอดคล้องกันและเชื่อถือได้ในอุปกรณ์ทุกเครื่อง
เราขอแนะนําลักษณะการทํางานของแอปดังต่อไปนี้
หากมีการออกอากาศ Intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGให้ทำดังนี้ระบบจะตัดการเชื่อมต่อลิงก์ ACL (การเชื่อมต่อแบบไม่ใช้การเชื่อมต่อแบบแอซิงโครนัส) แต่ระบบจะเก็บข้อมูลการเชื่อมโยงสำหรับอุปกรณ์ไว้ (ตามที่อธิบายไว้ที่นี่)
แอปของคุณควรใช้ Intent นี้เป็นสัญญาณหลักในการจับสัญญาณการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงและแนะนำผู้ใช้ให้ยืนยันว่าอุปกรณ์ระยะไกลอยู่ในระยะสัญญาณก่อนที่จะเริ่มการลืมอุปกรณ์หรือการจับคู่อีกครั้ง
หากอุปกรณ์ตัดการเชื่อมต่อหลังจากได้รับ
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGแอปของคุณควรระมัดระวังเกี่ยวกับการเชื่อมต่ออีกครั้ง เนื่องจากอุปกรณ์อาจไม่ได้จับคู่กับระบบแล้วหากไม่ได้ออกอากาศ Intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGลิงก์ ACL จะยังคงเชื่อมต่ออยู่ และระบบจะนำข้อมูลการเชื่อมโยงของอุปกรณ์ออก เช่นเดียวกับลักษณะการทำงานใน Android 15
ในกรณีนี้ แอปของคุณควรใช้กลไกการจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงที่มีอยู่ต่อไปเช่นเดียวกับใน Android รุ่นก่อนหน้า เพื่อตรวจหาและจัดการเหตุการณ์การสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยง
วิธีใหม่ในการนำการจับคู่บลูทูธออก
ตอนนี้แอปทั้งหมดที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 สามารถยกเลิกการจับคู่อุปกรณ์บลูทูธได้โดยใช้ API สาธารณะใน CompanionDeviceManager หากอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ร่วมกันได้รับการจัดการเป็นการเชื่อมโยง CDM แอปจะทริกเกอร์การนำการเชื่อมโยงบลูทูธออกได้โดยใช้ removeBond(int) API ใหม่ในอุปกรณ์ที่เชื่อมโยง แอปสามารถตรวจสอบการเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะการเชื่อมโยงได้โดยฟังเหตุการณ์การแพร่กระจายข้อมูลของอุปกรณ์บลูทูธ
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED
ความปลอดภัย
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงด้านความปลอดภัยต่อไปนี้
การล็อกดาวน์เวอร์ชัน MediaStore
สำหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ขึ้นไป MediaStore#getVersion() จะมีลักษณะเฉพาะสำหรับแต่ละแอป ซึ่งจะนําพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ระบุออกจากสตริงเวอร์ชันเพื่อป้องกันการละเมิดและการใช้เทคนิคการระบุตัวตน แอปไม่ควรคาดเดารูปแบบของเวอร์ชันนี้ แอปควรจัดการการเปลี่ยนแปลงเวอร์ชันอยู่แล้วเมื่อใช้ API นี้ และในกรณีส่วนใหญ่ก็ไม่จำเป็นต้องเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานปัจจุบัน เว้นแต่นักพัฒนาแอปจะพยายามอนุมานข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมที่อยู่นอกเหนือขอบเขตที่ตั้งใจไว้ของ API นี้
เจตนาที่ปลอดภัยกว่า
The Safer Intents feature is a multi-phase security initiative designed to improve the security of Android's intent resolution mechanism. The goal is to protect apps from malicious actions by adding checks during intent processing and filtering intents that don't meet specific criteria.
In Android 15 the feature focused on the sending app, now with Android 16, shifts control to the receiving app, allowing developers to opt-in to strict intent resolution using their app manifest.
Two key changes are being implemented:
Explicit Intents Must Match the Target Component's Intent Filter: If an intent explicitly targets a component, it should match that component's intent filter.
Intents Without an Action Cannot Match any Intent Filter: Intents that don't have an action specified shouldn't be resolved to any intent filter.
These changes only apply when multiple apps are involved and don't affect intent handling within a single app.
Impact
The opt-in nature means that developers must explicitly enable it in their app manifest for it to take effect. As a result, the feature's impact will be limited to apps whose developers:
- Are aware of the Safer Intents feature and its benefits.
- Actively choose to incorporate stricter intent handling practices into their apps.
This opt-in approach minimizes the risk of breaking existing apps that may rely on the current less-secure intent resolution behavior.
While the initial impact in Android 16 may be limited, the Safer Intents initiative has a roadmap for broader impact in future Android releases. The plan is to eventually make strict intent resolution the default behavior.
The Safer Intents feature has the potential to significantly enhance the security of the Android ecosystem by making it more difficult for malicious apps to exploit vulnerabilities in the intent resolution mechanism.
However, the transition to opt-out and mandatory enforcement must be carefully managed to address potential compatibility issues with existing apps.
Implementation
Developers need to explicitly enable stricter intent matching using the
intentMatchingFlags attribute in their app manifest.
Here is an example where the feature is opt-in for the entire app,
but disabled/opt-out on a receiver:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
More on the supported flags:
| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Enforces stricter matching for incoming intents |
| none | Disables all special matching rules for incoming intents. When specifying multiple flags, conflicting values are resolved by giving precedence to the "none" flag |
| allowNullAction | Relaxes the matching rules to allow intents without an action to match. This flag to be used in conjunction with "enforceIntentFilter" to achieve a specific behavior |
Testing and Debugging
When the enforcement is active, apps should function correctly if the intent
caller has properly populated the intent.
However, blocked intents will trigger warning log messages like
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" and "Access blocked:"
with the tag "PackageManager."
This indicates a potential issue that could impact the app and requires
attention.
Logcat filter:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
การกรอง Syscall ของ GPU
To harden the Mali GPU surface, Mali GPU IOCTLs that have been deprecated or are intended solely for GPU development have been blocked in production builds. Additionally, IOCTLs used for GPU profiling have been restricted to the shell process or debuggable applications. Refer to the SAC update for more details on the platform-level policy.
This change takes place on Pixel devices using the Mali GPU (Pixel 6-9). Arm
has provided official categorization of their IOCTLs in
Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst of their r54p2 release. This
list will continue to be maintained in future driver releases.
This change does not impact supported graphics APIs (including Vulkan and OpenGL), and is not expected to impact developers or existing applications. GPU profiling tools such as the Streamline Performance Analyzer and the Android GPU Inspector won't be affected.
Testing
If you see a SELinux denial similar to the following, it is likely your application has been impacted by this change:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
If your application needs to use blocked IOCTLs, please file a bug and assign it to android-partner-security@google.com.
FAQ
Does this policy change apply to all OEMs? This change will be opt-in, but available to any OEMs who would like to use this hardening method. Instructions for implementing the change can be found in the implementation documentation.
Is it mandatory to make changes in the OEM codebase to implement this, or does it come with a new AOSP release by default? The platform-level change will come with a new AOSP release by default. Vendors may opt-in to this change in their codebase if they would like to apply it.
Are SoCs responsible for keeping the IOCTL list up to date? For example, if my device uses an ARM Mali GPU, would I need to reach out to ARM for any of the changes? Individual SoCs must update their IOCTL lists per device upon driver release. For example, ARM will update their published IOCTL list upon driver updates. However, OEMs should make sure that they incorporate the updates in their SEPolicy, and add any selected custom IOCTLs to the lists as needed.
Does this change apply to all Pixel in-market devices automatically, or is a user action required to toggle something to apply this change? This change applies to all Pixel in-market devices using the Mali GPU (Pixel 6-9). No user action is required to apply this change.
Will use of this policy impact the performance of the kernel driver? This policy was tested on the Mali GPU using GFXBench, and no measurable change to GPU performance was observed.
Is it necessary for the IOCTL list to align with the current userspace and kernel driver versions? Yes, the list of allowed IOCTLs must be synchronized with the IOCTLs supported by both the userspace and kernel drivers. If the IOCTLs in the user space or kernel driver are updated, the SEPolicy IOCTL list must be updated to match.
ARM has categorized IOCTLs as 'restricted' / 'instrumentation', but we want to use some of them in production use-cases, and/or deny others. Individual OEMs/SoCs are responsible for deciding on how to categorize the IOCTLs they use, based on the configuration of their userspace Mali libraries. ARM's list can be used to help decide on these, but each OEM/SoC's use-case may be different.
ความเป็นส่วนตัว
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงด้านความเป็นส่วนตัวต่อไปนี้
สิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน
แอปที่มีINTERNETจะเข้าถึงอุปกรณ์ใน LAN ได้
ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ในพื้นที่ได้ง่าย แต่ก็มีผลกระทบด้านความเป็นส่วนตัวด้วย เช่น การสร้างลายนิ้วมือของผู้ใช้ และการเป็นพร็อกซีสำหรับตำแหน่ง
โปรเจ็กต์การปกป้องเครือข่าย LAN มีเป้าหมายเพื่อปกป้องความเป็นส่วนตัวของผู้ใช้โดย จำกัดการเข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN ไว้เบื้องหลังสิทธิ์รันไทม์ใหม่
แผนการเปิดตัว
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะเปิดตัวระหว่าง 2 รุ่น ได้แก่ 25Q2 และ 26Q2 ตามลำดับ นักพัฒนาแอปต้องปฏิบัติตามคำแนะนำนี้สำหรับ 25Q2 และแชร์ความคิดเห็น เนื่องจากระบบจะบังคับใช้การป้องกันเหล่านี้ใน Android รุ่นต่อๆ ไป นอกจากนี้ นักพัฒนาแอปจะต้องอัปเดตสถานการณ์ที่ขึ้นอยู่กับการเข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายในโดยนัยโดยใช้คำแนะนำต่อไปนี้ และเตรียมพร้อมสำหรับการปฏิเสธของผู้ใช้ และการเพิกถอนสิทธิ์ใหม่
ผลกระทบ
ในระยะปัจจุบัน LNP เป็นฟีเจอร์ที่ต้องเลือกใช้ ซึ่งหมายความว่าจะมีผลกับแอปที่เลือกใช้เท่านั้น เป้าหมายของระยะการเลือกใช้คือการช่วยให้นักพัฒนาแอป เข้าใจว่าส่วนใดของแอปที่ต้องอาศัยการเข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN โดยนัย เพื่อเตรียมพร้อมที่จะใช้การป้องกันสิทธิ์สำหรับส่วนดังกล่าวในการเปิดตัวครั้งถัดไป
แอปจะได้รับผลกระทบหากเข้าถึงเครือข่ายท้องถิ่นของผู้ใช้โดยใช้สิ่งต่อไปนี้
- การใช้ซ็อกเก็ตดิบโดยตรงหรือผ่านไลบรารีในที่อยู่เครือข่ายภายใน (เช่น โปรโตคอลการค้นพบบริการ mDNS หรือ SSDP)
- การใช้คลาสระดับเฟรมเวิร์กที่เข้าถึงเครือข่ายในเครื่อง (เช่น NsdManager)
การรับส่งข้อมูลไปยังและจากที่อยู่เครือข่ายภายในต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน ตารางต่อไปนี้แสดงกรณีที่พบบ่อย
| การดำเนินการเครือข่ายระดับต่ำของแอป | ต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน |
|---|---|
| สร้างการเชื่อมต่อ TCP ขาออก | ใช่ |
| ยอมรับการเชื่อมต่อ TCP ขาเข้า | ใช่ |
| การส่ง Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast แบบ UDP | ใช่ |
| การรับ Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast UDP ขาเข้า | ใช่ |
ข้อจำกัดเหล่านี้จะใช้ในส่วนลึกของสแต็กเครือข่าย จึงมีผลกับAPI เครือข่ายทั้งหมด ซึ่งรวมถึงซ็อกเก็ตที่สร้างขึ้นในโค้ดเนทีฟหรือโค้ดที่มีการจัดการ ไลบรารีเครือข่าย เช่น Cronet และ OkHttp รวมถึง API ใดๆ ที่ใช้งานอยู่บนไลบรารีเหล่านั้น การพยายามแก้ไขบริการใน เครือข่ายภายใน (เช่น บริการที่มีคำต่อท้าย .local) จะต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน
ข้อยกเว้นสำหรับกฎข้างต้น
- หากเซิร์ฟเวอร์ DNS ของอุปกรณ์อยู่ในเครือข่ายภายใน การรับส่งข้อมูลไปยังหรือจากเซิร์ฟเวอร์ดังกล่าว (ที่พอร์ต 53) ไม่จำเป็นต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน
- แอปพลิเคชันที่ใช้ตัวสลับเอาต์พุตเป็นเครื่องมือเลือกในแอปจะไม่ต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายในพื้นที่ (จะมีคำแนะนำเพิ่มเติมในไตรมาสที่ 4 ปี 2025)
คำแนะนำสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป (เลือกใช้)
หากต้องการเลือกใช้ข้อจำกัดเครือข่ายในเครื่อง ให้ทำดังนี้
- แฟลชอุปกรณ์เป็นบิลด์ที่มี 25Q2 เบต้า 3 ขึ้นไป
- ติดตั้งแอปที่จะทดสอบ
สลับสถานะ Appcompat ใน adb โดยทำดังนี้
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>รีบูตอุปกรณ์
ตอนนี้สิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN ของแอปถูกจำกัดแล้ว และการพยายามเข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN จะทำให้เกิดข้อผิดพลาดของซ็อกเก็ต หากคุณใช้ API ที่ ดำเนินการในเครือข่ายภายในนอกกระบวนการของแอป (เช่น NsdManager) API เหล่านี้จะไม่ได้รับผลกระทบในระหว่างระยะการเลือกใช้
หากต้องการกู้คืนสิทธิ์เข้าถึง คุณต้องให้สิทธิ์แอปในการเข้าถึง NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES
- ตรวจสอบว่าแอปประกาศสิทธิ์
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESในไฟล์ Manifest - ไปที่การตั้งค่า > แอป > [ชื่อแอปพลิเคชัน] > สิทธิ์ > อุปกรณ์ที่อยู่ใกล้เคียง > อนุญาต
ตอนนี้สิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN ของแอปควรได้รับการกู้คืนแล้ว และสถานการณ์ทั้งหมดควรทํางานได้เหมือนก่อนที่จะเลือกใช้แอป
เมื่อการบังคับใช้เพื่อการปกป้องเครือข่าย LAN เริ่มขึ้น การเข้าชมเครือข่ายของแอป จะได้รับผลกระทบดังนี้
| สิทธิ์ | คำขอ LAN ขาออก | คำขออินเทอร์เน็ตขาออก/ขาเข้า | คำขอ LAN ขาเข้า |
|---|---|---|---|
| ให้สิทธิ์ | Works | Works | Works |
| ไม่ให้สิทธิ์ | เรื่องหน้าแตก | Works | เรื่องหน้าแตก |
ใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้เพื่อเปิด/ปิด Flag App-Compat
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
ข้อผิดพลาด
ระบบจะส่งข้อผิดพลาดที่เกิดจากข้อจำกัดเหล่านี้กลับไปยังซ็อกเก็ตที่เรียกใช้ เมื่อใดก็ตามที่เรียกใช้ send หรือตัวแปร send ไปยังที่อยู่เครือข่ายภายใน
ตัวอย่างข้อผิดพลาด
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
คำจำกัดความของเครือข่ายภายใน
เครือข่ายภายในในโปรเจ็กต์นี้หมายถึงเครือข่าย IP ที่ใช้อินเทอร์เฟซเครือข่ายที่รองรับการออกอากาศ เช่น Wi-Fi หรืออีเทอร์เน็ต แต่ไม่รวมการเชื่อมต่อเซลลูลาร์ (WWAN) หรือ VPN
เครือข่ายต่อไปนี้ถือเป็นเครือข่ายท้องถิ่น
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // ลิงก์ภายใน
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- ลิงก์ภายใน
- เส้นทางที่เชื่อมต่อโดยตรง
- เครือข่าย Stub เช่น Thread
- หลายซับเน็ต (จะแจ้งภายหลัง)
นอกจากนี้ ทั้งที่อยู่แบบมัลติแคสต์ (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) และที่อยู่ IPv4 แบบบรอดแคสต์ (255.255.255.255) จะจัดเป็นที่อยู่เครือข่ายภายใน
รูปภาพที่เป็นของแอป
เมื่อแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมาย SDK 36 ขึ้นไปในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 16 ขึ้นไปแสดงข้อความแจ้งขอสิทธิ์เข้าถึงรูปภาพและวิดีโอ ผู้ใช้ที่เลือกจำกัดการเข้าถึงสื่อที่เลือกไว้จะเห็นรูปภาพทั้งหมดที่แอปเป็นเจ้าของซึ่งเลือกไว้ล่วงหน้าในเครื่องมือเลือกรูปภาพ ผู้ใช้สามารถยกเลิกการเลือกรายการที่เลือกไว้ล่วงหน้ารายการใดก็ได้ ซึ่งจะเป็นการเพิกถอนสิทธิ์เข้าถึงรูปภาพและวิดีโอเหล่านั้นของแอป
