پلتفرم اندروید ۱۶ شامل تغییرات رفتاری است که ممکن است بر برنامه شما تأثیر بگذارد. تغییرات رفتاری زیر برای همه برنامهها هنگام اجرا در اندروید ۱۶، صرف نظر از targetSdkVersion ، اعمال میشود. شما باید برنامه خود را آزمایش کنید و سپس در صورت لزوم، آن را برای پشتیبانی از این تغییرات، در صورت لزوم، اصلاح کنید.
حتماً فهرست تغییرات رفتاری که فقط بر برنامههای اندروید ۱۶ تأثیر میگذارند را نیز بررسی کنید.
عملکرد اصلی
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر است که قابلیتهای اصلی مختلف سیستم اندروید را اصلاح یا گسترش میدهد.
بهینهسازی سهمیهبندی JobScheduler
از Android 16 شروع میکنیم، ما سهمیه زمان اجرای کار را به طور منظم و سریع بر اساس عوامل زیر تنظیم میکنیم:
- برنامه در کدام سطل آماده به کار برنامه قرار دارد : در Android 16، سطل های آماده به کار فعال با یک سهمیه زمان اجرا سخاوتمندانه شروع به اجرا می کنند.
- اگر کار در حالی که برنامه در بالاترین وضعیت است اجرا شود : در Android 16، Jobs زمانی که برنامه برای کاربر قابل مشاهده است شروع می شود و پس از نامرئی شدن برنامه ادامه می یابد، به سهمیه زمان اجرای کار پایبند خواهد بود.
- اگر کار هنگام اجرای یک سرویس پیشزمینه اجرا میشود : در Android 16، کارهایی که همزمان با یک سرویس پیشزمینه اجرا میشوند، به سهمیه زمان اجرای کار پایبند هستند. اگر از کارهایی برای انتقال داده توسط کاربر استفاده می کنید، به جای آن از کارهای انتقال داده توسط کاربر استفاده کنید.
این تغییر بر وظایف برنامه ریزی شده با استفاده از WorkManager، JobScheduler و DownloadManager تأثیر می گذارد. برای رفع اشکال چرایی توقف کار، توصیه میکنیم با فراخوانی WorkInfo.getStopReason() ثبت کنید که چرا کارتان متوقف شده است (برای کارهای JobScheduler، با JobParameters.getStopReason() ) تماس بگیرید.
برای اطلاعات در مورد اینکه چگونه وضعیت برنامه شما بر منابعی که میتواند استفاده کند تأثیر میگذارد، به محدودیتهای منابع مدیریت نیرو مراجعه کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد بهترین شیوه های باتری بهینه، به راهنمای بهینه سازی استفاده از باتری برای API های زمان بندی کار مراجعه کنید.
همچنین توصیه میکنیم از API جدید JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory که در اندروید 16 معرفی شده است استفاده کنید تا بفهمید چرا یک کار اجرا نشده است.
تست کردن
برای آزمایش رفتار برنامهتان، میتوانید تا زمانی که برنامه روی دستگاه Android 16 اجرا میشود، برخی بهینهسازیهای سهمیه شغلی را لغو کنید.
برای غیرفعال کردن اجرای "نقطه بالا به سهمیه زمان اجرا پایبند خواهد بود"، دستور adb زیر را اجرا کنید:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
برای غیرفعال کردن اجرای «کارهایی که همزمان با یک سرویس پیشزمینه اجرا میشوند، به سهمیه زمان اجرای کار پایبند هستند»، دستور adb زیر را اجرا کنید:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
برای آزمایش رفتار سطل آماده به کار برنامه خاص، می توانید با استفاده از دستور adb زیر، سطل استندبای برنامه برنامه خود را تنظیم کنید:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
برای درک سطل استندبای برنامه که برنامه شما در آن قرار دارد، میتوانید با استفاده از دستور adb زیر، سطل استندبای برنامه برنامه خود را دریافت کنید:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
دلیل توقف مشاغل خالی رها شده
An abandoned job occurs when the JobParameters object associated with the job
has been garbage collected, but JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) has not been called to signal job completion. This indicates that
the job may be running and being rescheduled without the app's awareness.
Apps that rely on JobScheduler, don't maintain a strong reference to the
JobParameters object, and timeout will now be granted the new job stop reason
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, instead of STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
If there are frequent occurrences of the new abandoned stop reason, the system will take mitigation steps to reduce job frequency.
Apps should use the new stop reason to detect and reduce abandoned jobs.
If you're using WorkManager, AsyncTask, or DownloadManager, you aren't impacted because these APIs manage the job lifecycle on your app's behalf.
JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground کاملاً منسوخ شده است
The JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean)
method indicates the importance of a job while the scheduling app is in the
foreground or when temporarily exempted from background restrictions.
This method has been deprecated since Android 12 (API level 31). Starting in Android 16, it no longer functions effectively and calling this method will be ignored.
This removal of functionality also applies to
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). Starting in Android
16, if the method is called, the method returns false.
محدوده اولویت پخش مرتبشده دیگر سراسری نیست
Android apps are allowed to define priorities on broadcast receivers to control
the order in which the receivers receive and process the broadcast. For
manifest-declared receivers, apps can use the
android:priority attribute to define the priority and for
context-registered receivers, apps can use the
IntentFilter#setPriority() API to define the priority. When
a broadcast is sent, the system delivers it to receivers in order of their
priority, from highest to lowest.
In Android 16, broadcast delivery order using the android:priority attribute
or IntentFilter#setPriority() across different processes will not be
guaranteed. Broadcast priorities will only be respected within the same
application process rather than across all processes.
Also, broadcast priorities will be automatically confined to the range
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Only system components will be
allowed to set SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY as broadcast
priority.
Your app might be impacted if it does either of the following:
- Your application has declared multiple processes with the same broadcast intent, and has expectations around receiving those intents in a certain order based on the priority.
- Your application process interacts with other processes and has expectations around receiving a broadcast intent in a certain order.
If the processes need to coordinate with each other, they should communicate using other coordination channels.
تغییرات داخلی ART
Android 16 includes the latest updates to the Android Runtime (ART) that improve the Android Runtime's (ART's) performance and provide support for additional Java features. Through Google Play System updates, these improvements are also available to over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher.
As these changes are released, libraries and app code that rely on internal structures of ART might not work correctly on devices running Android 16, along with earlier Android versions that update the ART module through Google Play system updates.
Relying on internal structures (such as non-SDK interfaces) can always lead to compatibility problems, but it's particularly important to avoid relying on code (or libraries containing code) that leverages internal ART structures, since ART changes aren't tied to the platform version the device is running on and they go out to over a billion devices through Google Play system updates.
All developers should check whether their app is impacted by testing their apps thoroughly on Android 16. In addition, check the known issues to see if your app depends on any libraries that we've identified that rely on internal ART structures. If you do have app code or library dependencies that are affected, seek public API alternatives whenever possible and request public APIs for new use cases by creating a feature request in our issue tracker.
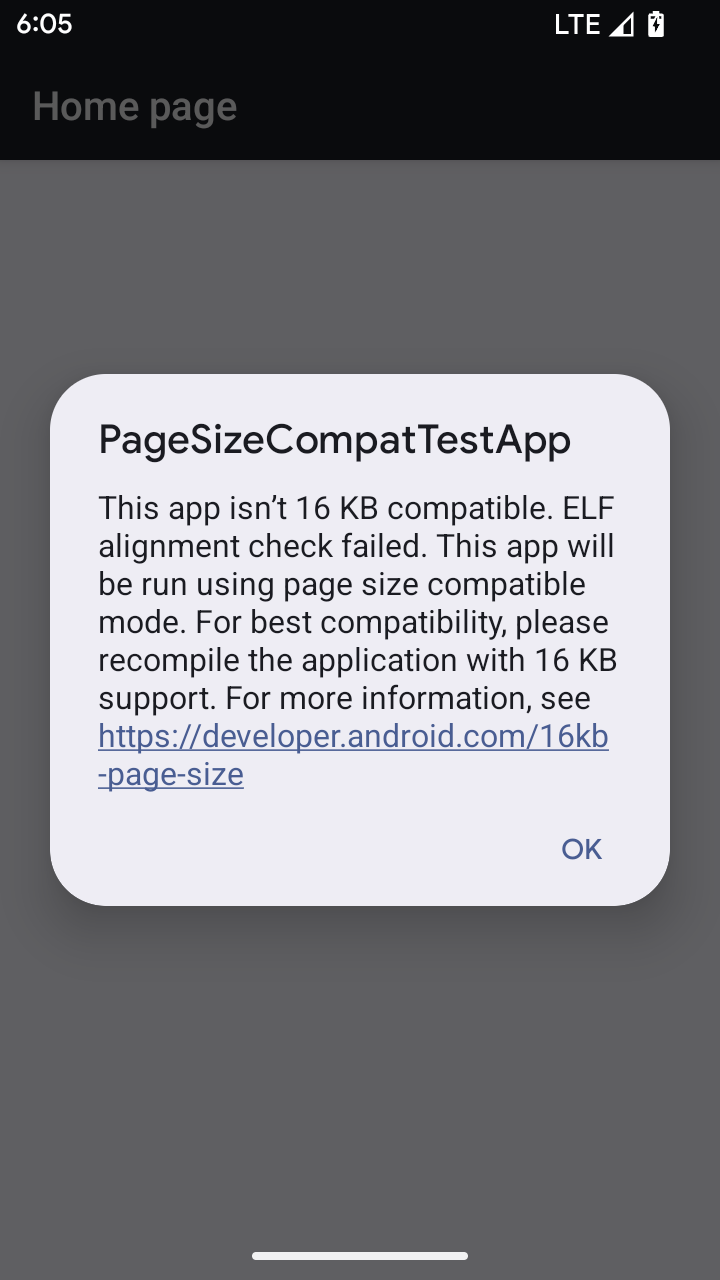
حالت سازگاری با اندازه صفحه ۱۶ کیلوبایت
Android 15 introduced support for 16 KB memory pages to optimize performance of the platform. Android 16 adds a compatibility mode, allowing some apps built for 4 KB memory pages to run on a device configured for 16 KB memory pages.
When your app is running on a device with Android 16 or higher, if Android
detects that your app has 4 KB aligned memory pages, it automatically uses
compatibility mode and display a notification dialog to the user. Setting the
android:pageSizeCompat property in the AndroidManifest.xml to enable the
backwards compatibility mode will prevent the display of the dialog when your
app launches. To use the android:pageSizeCompat property, compile your app
using the Android 16 SDK.
For best performance, reliability, and stability, your app should still be 16 KB aligned. Check out our recent blog post on updating your apps to support 16 KB memory pages for more details.
تجربه کاربری و رابط کاربری سیستم
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر است که برای ایجاد یک تجربه کاربری سازگارتر و شهودیتر در نظر گرفته شدهاند.
بیاعتبار کردن اعلانهای اختلال در دسترسیپذیری
Android 16 deprecates accessibility announcements, characterized by the use of
announceForAccessibility or the dispatch of
TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT accessibility events. These can create
inconsistent user experiences for users of TalkBack and Android's screen reader,
and alternatives better serve a broader range of user needs across a variety of
Android's assistive technologies.
Examples of alternatives:
- For significant UI changes like window changes, use
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)andsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - To inform the user of changes to critical UI, use
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. These should be used sparingly as they may generate announcements every time a View is updated. - To notify users about errors, send an
AccessibilityEventof typeAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORand setAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence), or useTextView#setError(CharSequence).
The reference documentation for the deprecated
announceForAccessibility API includes more details about
suggested alternatives.
پشتیبانی از ناوبری سه دکمهای
Android 16 brings predictive back support to the 3-button navigation for apps that have properly migrated to predictive back. Long-pressing the back button initiates a predictive back animation, giving you a preview of where the back swipe takes you.
This behavior applies across all areas of the system that support predictive back animations, including the system animations (back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity).
آیکونهای برنامه با تم خودکار
Beginning with Android 16 QPR 2, Android automatically applies themes to app icons to create a cohesive home screen experience. This occurs if an app does not provide its own themed app icon. Apps can control the design of their themed app icon by including a monochrome layer within their adaptive icon and previewing what their app icon will look like in Android Studio.
فاکتورهای شکل دستگاه
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر برای برنامهها هنگام نمایش روی نمایشگرها توسط دارندگان دستگاههای مجازی است.
مالک دستگاه مجازی لغو میکند
A virtual device owner is a trusted or privileged app that creates and manages a virtual device. Virtual device owners run apps on a virtual device and then project the apps to the display of a remote device, such as a personal computer, virtual reality device, or car infotainment system. The virtual device owner is on a local device, such as a mobile phone.
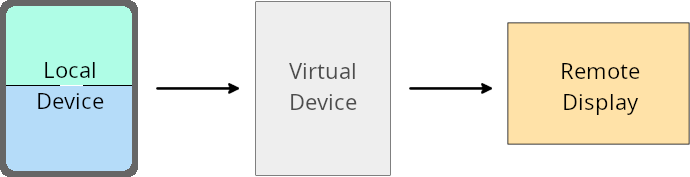
Per-app overrides
On devices running Android 16 (API level 36), virtual device owners can override app settings on select virtual devices that the virtual device owners manage. For example, to improve app layout, a virtual device owner can ignore orientation, aspect ratio, and resizability restrictions when projecting apps onto an external display.
Common breaking changes
The Android 16 behavior might impact your app's UI on large screen form factors such as car displays or Chromebooks, especially layouts that were designed for small displays in portrait orientation. To learn how to make your app adaptive for all device form factors, see About adaptive layouts.
References
امنیت
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییراتی است که امنیت سیستم را ارتقا میدهد تا به محافظت از برنامهها و کاربران در برابر برنامههای مخرب کمک کند.
امنیت بهبود یافته در برابر حملات تغییر مسیر Intent
Android 16 provides default security against general Intent redirection
attacks, with minimum compatibility and developer changes required.
We are introducing by-default security hardening solutions to Intent
redirection exploits. In most cases, apps that use intents normally won't
experience any compatibility issues; we've gathered metrics throughout our
development process to monitor which apps might experience breakages.
Intent redirection in Android occurs when an attacker can partly or fully control the contents of an intent used to launch a new component in the context of a vulnerable app, while the victim app launches an untrusted sub-level intent in an extras field of an ("top-level") Intent. This can lead to the attacker app launching private components in the context of the victim app, triggering privileged actions, or gaining URI access to sensitive data, potentially leading to data theft and arbitrary code execution.
Opt out of Intent redirection handling
Android 16 introduces a new API that allows apps to opt out of launch security protections. This might be necessary in specific cases where the default security behavior interferes with legitimate app use cases.
For applications compiling against Android 16 (API level 36) SDK or higher
You can directly use the removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method on the Intent
object.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
For applications compiling against Android 15 (API level 35) or lower
While not recommended, you can use reflection to access the
removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
برنامههای همراه دیگر از زمانهای کشف مطلع نمیشوند
Android 16 introduces a new behavior during
companion device pairing flow to protect the user's location
privacy from malicious apps. All companion apps running on Android 16 are no
longer directly notified of discovery timeout using
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Instead, the user is
notified of timeout events with a visual dialog. When the user dismisses
the dialog, the app is alerted of the association failure with
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
The search duration has also been extended from the original 20 seconds, and the device discovery can be stopped by the user at any point during the search. If at least one device was discovered within the first 20 seconds of starting the search, the CDM stops searching for additional devices.
اتصال
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر در پشته بلوتوث برای بهبود اتصال با دستگاههای جانبی است.
بهبود مدیریت ضرر اوراق قرضه
Starting in Android 16, the Bluetooth stack has been updated to improve security and user experience when a remote bond loss is detected. Previously, the system would automatically remove the bond and initiate a new pairing process, which could lead to unintentional re-pairing. We have seen in many instances apps not taking care of the bond loss event in a consistent way.
To unify the experience, Android 16 improved the bond loss handling to the system. If a previously bonded Bluetooth device could not be authenticated upon reconnection, the system will disconnect the link, retain local bond information, and display a system dialog informing users of the bond loss and directing them to re-pair.

