Android 15 offre aux développeurs de nouvelles fonctionnalités et API de qualité. Les sections suivantes résument ces fonctionnalités pour vous aider à vous familiariser avec les API associées.
Pour obtenir une liste détaillée des API ajoutées, modifiées et supprimées, consultez le rapport de différences des API. Pour en savoir plus sur les API ajoutées, consultez la documentation de référence des API Android. Pour Android 15, recherchez les API ajoutées au niveau d'API 35. Pour savoir dans quels domaines les changements de plate-forme peuvent affecter vos applications, consultez les modifications de comportement d'Android 15 pour les applications ciblant Android 15 et pour toutes les applications.
Appareil photo et médias
Android 15 inclut diverses fonctionnalités qui améliorent l'expérience de l'appareil photo et des contenus multimédias, et qui vous donnent accès à des outils et du matériel pour aider les créateurs à donner vie à leur vision sur Android.
Pour en savoir plus sur les dernières fonctionnalités et solutions pour les développeurs concernant les caméras et les contenus multimédias Android, consultez la conférence Créer des expériences multimédias et de caméras Android modernes de Google I/O.
Amplification luminosité faible
Android 15 introduit l'amplification de la luminosité, un mode d'exposition automatique disponible à la fois pour Camera 2 et l'extension de l'appareil photo en mode Nuit. L'amplification de la luminosité ajuste l'exposition du flux d'aperçu en cas de faible luminosité. Cela diffère de la façon dont l'extension d'appareil photo du mode Nuit crée des images fixes, car le mode Nuit combine une rafale de photos pour créer une seule image améliorée. Bien que le mode Nuit soit très efficace pour créer une image fixe, il ne peut pas créer un flux continu de frames, contrairement au mode Boost en faible luminosité. Ainsi, la fonctionnalité Boost en basse luminosité active les fonctionnalités de l'appareil photo, telles que:
- Fournir un aperçu amélioré des images pour que les utilisateurs puissent mieux cadrer leurs photos prises en basse luminosité
- Scanner des codes QR dans des conditions de faible luminosité
Si vous activez la fonctionnalité Boost en cas de faible luminosité, elle s'active automatiquement lorsque le niveau de luminosité est faible et se désactive lorsque la luminosité est plus élevée.
Les applications peuvent enregistrer le flux d'aperçu par faible luminosité dans le but d'éclaircir les vidéos.
Pour en savoir plus, consultez la section Amélioration en basse luminosité.
Commandes de la caméra dans l'application
Android 15 ajoute une extension pour un meilleur contrôle du matériel de l'appareil photo et de ses algorithmes sur les appareils compatibles:
- Ajustements avancés de l'intensité du flash permettant de contrôler précisément l'intensité du flash en mode
SINGLEetTORCHlors de la prise de vue.
Contrôle de la marge HDR
Android 15 choisit la plage dynamique appropriée pour les fonctionnalités de l'appareil sous-jacent et la profondeur de bits du panneau. Pour les pages contenant beaucoup de contenu SDR, comme une application de messagerie affichant une seule vignette HDR, ce comportement peut avoir un impact négatif sur la luminosité perçue du contenu SDR. Android 15 vous permet de contrôler la plage dynamique HDR avec setDesiredHdrHeadroom pour trouver un équilibre entre le contenu SDR et HDR.
Contrôle du volume

Android 15 est compatible avec la norme de volume CTA-2075 pour vous aider à éviter les incohérences de volume audio et à vous assurer que les utilisateurs n'ont pas à ajuster constamment le volume lorsqu'ils passent d'un contenu à un autre. Le système exploite les caractéristiques connues des appareils de sortie (écouteurs et haut-parleurs) ainsi que les métadonnées de volume disponibles dans le contenu audio AAC pour ajuster intelligemment le volume audio et les niveaux de compression de la plage dynamique.
Pour activer cette fonctionnalité, vous devez vous assurer que les métadonnées de volume sont disponibles dans votre contenu AAC et activer la fonctionnalité de la plate-forme dans votre application. Pour ce faire, vous instanciez un objet LoudnessCodecController en appelant sa méthode d'usine create avec l'ID de session audio de l'AudioTrack associé. Les mises à jour audio sont alors automatiquement appliquées. Vous pouvez transmettre
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener pour modifier ou filtrer
paramètres de volume sonore avant de les appliquer
MediaCodec
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
ExoPlayer sera également mis à jour pour AndroidX media3 afin d'utiliser
LoudnessCodecController pour une intégration parfaite des applications.
Appareils MIDI 2.0 virtuels
Android 13 est compatible avec la connexion à des appareils MIDI 2.0 via USB, qui communiquent à l'aide de paquets MIDI universels (UMP). Android 15 étend la compatibilité avec UMP aux applications MIDI virtuelles, ce qui permet aux applications de composition de contrôler les applications de synthétiseur en tant qu'appareil MIDI 2.0 virtuel, comme elles le feraient avec un appareil USB MIDI 2.0.
Décodage logiciel AV1 plus efficace

dav1d, le populaire décodeur logiciel AV1 de VideoLAN, est disponible pour les appareils Android qui ne prennent pas en charge le décodage AV1 en matériel. dav1d est jusqu'à trois fois plus performant que l'ancien décodeur logiciel AV1, ce qui permet de lire des vidéos AV1 HD pour plus d'utilisateurs, y compris sur certains appareils de milieu de gamme.
Votre application doit activer l'utilisation de dav1d en l'appelant par nom "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". dav1d deviendra le décodeur logiciel AV1 par défaut lors d'une mise à jour ultérieure. Cette compatibilité est standardisée et rétroportée vers les appareils Android 11 qui reçoivent des mises à jour du système Google Play.
Productivité et outils pour les développeurs
Bien que la plupart de nos efforts pour améliorer votre productivité soient axés sur des outils tels qu'Android Studio, Jetpack Compose et les bibliothèques Android Jetpack, nous cherchons toujours des moyens de vous aider à concrétiser plus facilement votre vision sur la plate-forme.
Mises à jour OpenJDK 17
Android 15 poursuit le travail d'actualisation des principales bibliothèques Android afin de s'adapter aux fonctionnalités des dernières versions d'OpenJDK LTS.
Les principales fonctionnalités et améliorations sont les suivantes:
- Améliorations de la qualité de vie concernant les tampons NIO
- Flux
- Méthodes
mathetstrictmathsupplémentaires - Mises à jour de packages
util, y compriscollection,mapetsetséquentielles - Compatibilité avec
ByteBufferdansDeflater - Mises à jour de sécurité telles que
X500PrivateCredentialet mises à jour de clés de sécurité
Ces API sont mises à jour sur plus d'un milliard d'appareils exécutant Android 12 (niveau d'API 31) ou version ultérieure via les mises à jour du système Google Play, ce qui vous permet de cibler les dernières fonctionnalités de programmation.
Améliorations apportées aux PDF
Android 15 apporte d'importantes améliorations au PdfRenderer
API. Les applications peuvent intégrer des fonctionnalités avancées telles que l'affichage
fichiers protégés par mot de passe, annotations, modification de formulaires,
recherche et sélection avec texte. PDF linéarisé
des optimisations sont prises en charge pour accélérer l'affichage des PDF locaux et réduire l'utilisation des ressources.
La bibliothèque PDF Jetpack utilise ces API pour simplifier l'ajout de PDF
à votre application.

PdfRenderer a été déplacé vers un module pouvant être mis à jour à l'aide de Google
mises à jour du système Play indépendamment de la version de la plate-forme, et nous acceptons
pour revenir à Android 11 (niveau d'API 30) en créant un
version de la surface d'API antérieure à Android 15, appelée
PdfRendererPreV
Améliorations apportées au changement de langue automatique
Android 14 a ajouté la reconnaissance multilingue sur l'appareil dans l'audio avec le basculement automatique entre les langues, mais cela peut entraîner la suppression de mots, en particulier lorsque les langues changent avec moins de pause entre les deux énoncés. Android 15 ajoute des commandes supplémentaires pour aider les applications à adapter ce changement à leur cas d'utilisation.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS limite le changement automatique au début de la session audio, tandis que EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES désactive le changement de langue après un nombre défini de changements. Ces options sont particulièrement utiles si vous prévoyez qu'une seule langue sera parlée pendant la session et qu'elle doit être détectée automatiquement.
Amélioration de l'API OpenType Variable Font
Android 15 améliore la facilité d'utilisation de la police variable OpenType. Vous pouvez créer
Une instance FontFamily à partir d'une police variable sans spécifier d'axes de pondération
avec l'API buildVariableFamily. Le moteur de rendu du texte remplace la valeur de l'axe wght pour qu'elle corresponde au texte affiché.
L'utilisation de l'API simplifie considérablement le code permettant de créer un Typeface:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Auparavant, pour créer le même Typeface, vous aviez besoin de beaucoup plus de code:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Voici un exemple de rendu d'un Typeface créé avec les anciennes et nouvelles API :
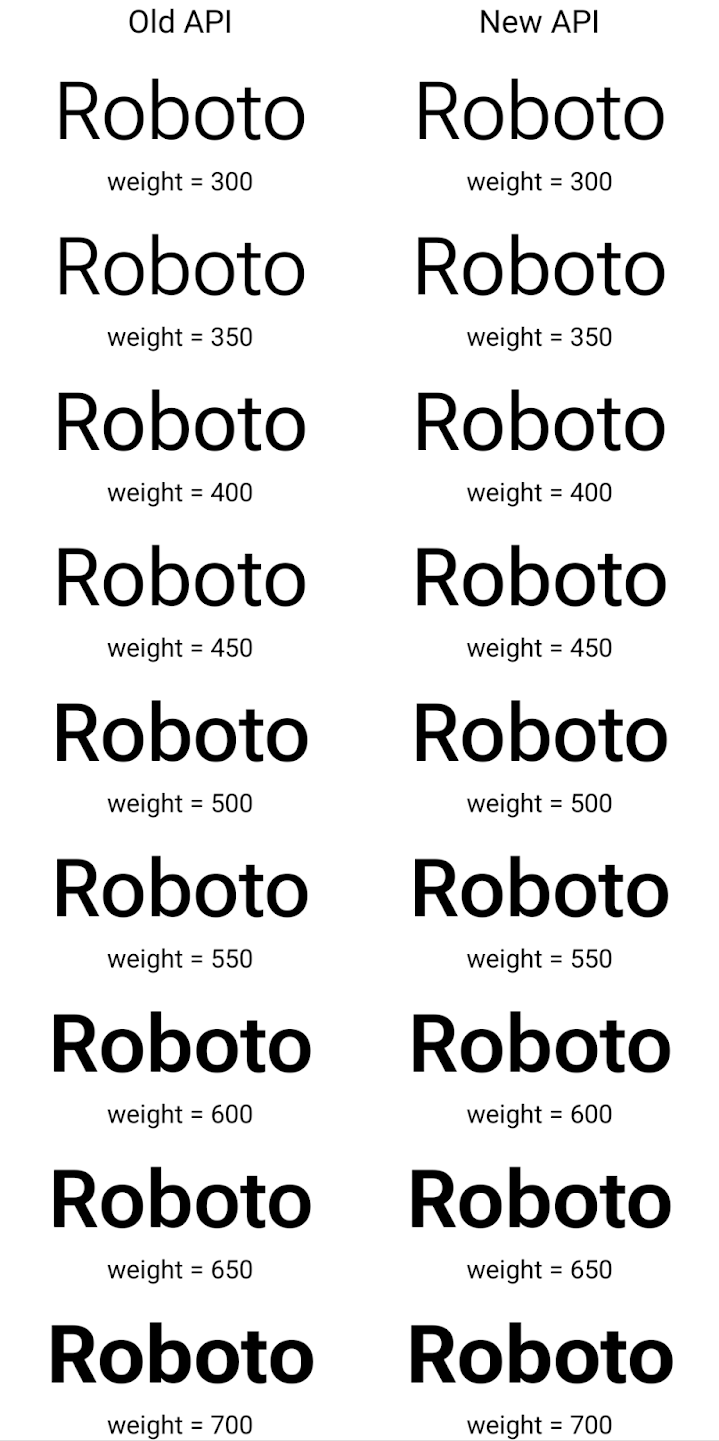
Dans cet exemple, le Typeface créé avec l'ancienne API n'est pas en mesure de créer des épaisseurs de police précises pour les instances Font 350, 450, 550 et 650. Le moteur de rendu utilise donc l'épaisseur la plus proche. Dans ce cas, 300 est affiché au lieu de 350, 400 au lieu de 450, etc. En revanche, le Typeface créé avec les nouvelles API crée dynamiquement une instance Font pour un poids donné. Les poids précis sont donc affichés pour 350, 450, 550 et 650 également.
Contrôles précis des sauts de ligne
À partir d'Android 15, un TextView et le séparateur de ligne sous-jacent peuvent conserver la partie de texte donnée sur la même ligne pour améliorer la lisibilité. Vous pouvez profiter de cette personnalisation de la casse en utilisant la balise <nobreak> dans les ressources de chaîne ou createNoBreakSpan. De même, vous pouvez empêcher la césure des mots à l'aide de la balise <nohyphen> ou createNoHyphenationSpan.
Par exemple, la ressource de chaîne suivante n'inclut pas de saut de ligne et s'affiche avec le texte "Pixel 8 Pro." qui se brise à un endroit indésirable:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
En revanche, cette ressource de chaîne inclut la balise <nobreak>, qui affiche la phrase "Pixel 8 Pro" et empêche les sauts de ligne:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
La différence d'affichage de ces chaînes est illustrée dans les images suivantes:

<nobreak>.
<nobreak>.Archivage des applications
Android et Google Play ont annoncé la prise en charge de l'archivage des applications l'année dernière, ce qui permet aux utilisateurs de libérer de l'espace en supprimant partiellement les applications peu utilisées de l'appareil publiées à l'aide d'Android App Bundle sur Google Play. Android 15 prend en charge l'archivage des applis au niveau de l'OS et le désarchivage, ce qui facilite son implémentation pour toutes les plates-formes de téléchargement d'applications.
Les applications disposant de l'autorisation REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES peuvent appeler la
PackageInstaller requestArchive pour demander l'archivage d'une
le package d'application installé, qui supprime l'APK et tous les fichiers mis en cache, mais persiste
données utilisateur. Les applications archivées sont renvoyées en tant qu'applications pouvant être affichées via les API LauncherApps. Les utilisateurs verront un traitement de l'UI pour mettre en évidence que ces applications sont archivées. Si un utilisateur appuie sur une application archivée, le programme d'installation responsable
reçoivent une demande de désarchivage. Le processus de restauration peut être
surveillée par l'annonce ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED.
Activer le mode 16 ko sur un appareil à l'aide des options pour les développeurs

Activez l'option pour les développeurs Démarrer avec une page de 16 kB pour démarrer un appareil en mode 16 kB.
Dans les versions QPR d'Android 15, vous pouvez utiliser l'option pour les développeurs disponible sur certains appareils pour démarrer l'appareil en mode 16 Ko et effectuer des tests sur l'appareil. Avant d'utiliser l'option pour les développeurs, accédez à Paramètres > Système > Mises à jour logicielles et appliquez les mises à jour disponibles.
Cette option pour les développeurs est disponible sur les appareils suivants :
Pixel 8 et 8 Pro (avec Android 15 QPR1 ou version ultérieure)
Pixel 8a (avec Android 15 QPR1 ou version ultérieure)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro et 9 Pro XL (avec Android 15 QPR2 bêta 2 ou version ultérieure)
Graphiques
Android 15 apporte les dernières améliorations graphiques, y compris ANGLE et des ajouts au système graphique Canvas.
Moderniser l'accès au GPU d'Android

Le matériel Android a beaucoup évolué depuis les premiers jours, où le noyau de l'OS s'exécutait sur un seul CPU et que les GPU étaient accessibles à l'aide d'API basées sur des pipelines à fonction fixe. L'API graphique Vulkan® est disponible dans le NDK depuis Android 7.0 (niveau d'API 24) avec une abstraction de bas niveau qui reflète mieux le matériel GPU moderne, s'adapte mieux pour prendre en charge plusieurs cœurs de processeur et offre une surcharge de pilote de processeur réduite, ce qui améliore les performances des applications. Vulkan est compatible avec tous les moteurs de jeu modernes.
Vulkan est l'interface préférée d'Android pour le GPU. Par conséquent, Android 15 inclut ANGLE en tant que couche facultative pour exécuter OpenGL® ES sur Vulkan. Le passage à ANGLE permettra de normaliser l'implémentation OpenGL Android pour améliorer la compatibilité et, dans certains cas, les performances. Vous pouvez tester la stabilité et les performances de votre application OpenGL ES avec ANGLE en activant l'option pour les développeurs dans Settings -> System -> Developer Options -> Experimental: Enable ANGLE (Paramètres -> Système -> Options pour les développeurs -> Expérimental : Activer ANGLE) sur Android 15.
Feuille de route Android ANGLE sur Vulkan

Dans le cadre de la simplification de notre pile GPU, nous allons désormais fournir ANGLE en tant que pilote système GL sur davantage de nouveaux appareils, avec l'espoir qu'OpenGL/ES ne sera disponible que via ANGLE à l'avenir. Cela dit, nous prévoyons de continuer à prendre en charge OpenGL ES sur tous les appareils.
Étapes suivantes recommandées
Utilisez les options pour les développeurs pour sélectionner le pilote ANGLE pour OpenGL ES et tester votre application. Pour les nouveaux projets, nous vous recommandons vivement d'utiliser Vulkan pour C/C++.
Améliorations apportées à Dessin
Android 15 poursuit la modernisation du système graphique Canvas d'Android avec des fonctionnalités supplémentaires:
Matrix44fournit une matrice 4x4 pour transformer les coordonnées à utiliser lorsque vous souhaitez manipuler le canevas en 3D.clipShadercroise le clip actuel avec le nuanceur spécifié, tandis queclipOutShaderdéfinit le clip sur la différence entre le clip actuel et le nuanceur, chacun traitant le nuanceur comme un masque alpha. Cela permet de dessiner efficacement des formes complexes.
Performances et batterie
Android continue de vous aider à améliorer les performances et la qualité de vos applications. Android 15 introduit des API qui permettent d'exécuter plus efficacement les tâches dans votre application, d'optimiser les performances de l'application et de recueillir des insights sur vos applications.
Pour découvrir les bonnes pratiques en matière d'efficacité de la batterie, le débogage de l'utilisation du réseau et de l'alimentation, et des informations détaillées sur la façon dont nous améliorons l'efficacité de la batterie pour les tâches en arrière-plan dans Android 15 et les versions récentes d'Android, consultez la conférence Améliorer l'efficacité de la batterie pour les tâches en arrière-plan sur Android de Google I/O.
API ApplicationStartInfo
Dans les versions précédentes d'Android, le démarrage des applications était un peu mystérieux. Il était difficile de déterminer dans votre application si elle a démarré à partir d'un état à froid, tiède ou chaud. Il était également difficile de savoir combien de temps votre application a passé pendant les différentes phases de lancement: forking du processus, appel de onCreate, dessin du premier frame, etc. Lorsque votre classe Application a été instanciée, vous ne pouviez pas savoir si l'application a démarré à partir d'une diffusion, d'un fournisseur de contenu, d'une tâche, d'une sauvegarde, d'un démarrage terminé, d'une alarme ou d'un Activity.
L'API ApplicationStartInfo sur Android 15 fournit tout cela et plus encore. Vous pouvez même choisir d'ajouter vos propres codes temporels dans le flux pour collecter les données temporelles au même endroit. En plus de collecter des métriques, vous pouvez utiliser ApplicationStartInfo pour optimiser directement le démarrage de l'application. Par exemple, vous pouvez éliminer l'instanciation coûteuse des bibliothèques liées à l'UI dans votre classe Application lorsque votre application démarre en raison d'une diffusion.
Informations détaillées sur la taille de l'application
Depuis Android 8.0 (niveau d'API 26), Android inclut l'API StorageStats.getAppBytes, qui résume la taille installée d'une application en un seul nombre d'octets, qui correspond à la somme de la taille de l'APK, de la taille des fichiers extraits de l'APK et des fichiers générés sur l'appareil, tels que le code compilé à l'avance (AOT). Ce nombre n'est pas très révélateur de la façon dont votre application utilise l'espace de stockage.
Android 15 ajoute l'API StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]), qui vous permet d'obtenir des informations sur la façon dont votre application utilise tout cet espace, y compris les fractionnements de fichiers APK, le code lié à l'AOT et à l'accélération, les métadonnées dex, les bibliothèques et les profils guidés.
Profilage géré par l'application
Android 15 inclut la classe ProfilingManager, qui vous permet de collecter des informations de profilage à partir de votre application, telles que des empreintes de mémoire, des profils de segments de mémoire, des échantillons de pile, etc. Elle permet de rappeler à votre application un tag permettant d'identifier le fichier de sortie, qui est envoyé au répertoire de fichiers de votre application. L'API limite le débit pour minimiser l'impact sur les performances.
Pour simplifier la création de requêtes de profilage dans votre application, nous vous recommandons d'utiliser l'API AndroidX Profiling correspondante, disponible dans Core 1.15.0-rc01 ou version ultérieure.
Améliorations de la base de données SQLite
Android 15 introduit les API SQLite qui exposent les fonctionnalités avancées du SQLite sous-jacent qui ciblent des problèmes de performances spécifiques manifeste dans les applications. Ces API sont incluses dans la mise à jour de SQLite vers 3.44.3.
Les développeurs doivent consulter les bonnes pratiques concernant les performances de SQLite. pour exploiter pleinement leur base de données SQLite, en particulier lorsqu'ils travaillent avec de grands ou lors de l'exécution de requêtes sensibles à la latence.
- Transactions différées en lecture seule: lors de l'émission de transactions qui sont
en lecture seule (pas les instructions d'écriture), utilisez
beginTransactionReadOnly()etbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)pour émettre des transactionsDEFERREDen lecture seule. Ces transactions peuvent s'exécuter simultanément les unes avec les autres. Si la base de données est en mode WAL, elles peuvent s'exécuter simultanément avec des transactionsIMMEDIATEouEXCLUSIVE. - Nombre et ID de lignes : des API ont été ajoutées pour récupérer le nombre de lignes modifiées ou l'ID de la dernière ligne insérée sans émettre de requête supplémentaire.
getLastChangedRowCount()renvoie le nombre de lignes ont été insérées, mises à jour ou supprimées par l'instruction SQL la plus récente dans la transaction en cours, tandis quegetTotalChangedRowCount()renvoie le nombre défini pour la connexion en cours.getLastInsertRowId()renvoie l'rowidde la dernière ligne. à insérer sur la connexion actuelle. - Instructions brutes : émettez une instruction SQlite brute, en contournant les wrappers pratiques et tout coût de traitement supplémentaire qu'ils pourraient entraîner.
Mises à jour du Framework de performances dynamiques Android
Android 15 poursuit notre investissement dans le Framework de performances dynamiques Android (ADPF), un ensemble d'API permettant aux jeux et aux applications haute performance d'interagir plus directement avec les systèmes d'alimentation et thermiques des appareils Android. Sur les appareils compatibles, Android 15 ajoute des fonctionnalités ADPF:
- Un mode d'économie d'énergie pour les sessions d'indices afin d'indiquer que leurs threads associés doivent privilégier l'économie d'énergie aux performances, ce qui est idéal pour les charges de travail en arrière-plan de longue durée.
- Les durées de travail du GPU et du CPU peuvent toutes deux être signalées dans les sessions d'indices, ce qui permet au système d'ajuster les fréquences du CPU et du GPU ensemble pour mieux répondre aux exigences de la charge de travail.
- Seuils de plage de température pour interpréter l'état de limitation thermique possible en fonction de la prévision de la plage de température.
Pour en savoir plus sur l'utilisation de l'ADPF dans vos applications et jeux, consultez la documentation.
Confidentialité
Android 15 inclut diverses fonctionnalités qui aident les développeurs d'applications à protéger la confidentialité des utilisateurs.
Détection des enregistrements d'écran
Android 15 est désormais compatible avec les applications qui détectent que pendant leur enregistrement. Un rappel est appelé chaque fois que l'application passe de l'état visible à l'état invisible dans un enregistrement d'écran. Une application est considérée comme visible si des activités appartenant à l'UID du processus d'enregistrement sont enregistrées. Ainsi, si votre application effectue une opération sensible, peuvent informer l'utilisateur qu'ils sont enregistrés.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
Fonctionnalités IntentFilter étendues
Android 15 prend en charge une résolution Intent plus précise via UriRelativeFilterGroup, qui contient un ensemble d'objets UriRelativeFilter qui forment un ensemble de règles de correspondance Intent qui doivent toutes être satisfaites, y compris les paramètres de requête d'URL, les fragments d'URL et les règles de blocage ou d'exclusion.
Ces règles peuvent être définies dans le fichier XML AndroidManifest avec la balise <uri-relative-filter-group>, qui peut éventuellement inclure une balise android:allow. Ces balises peuvent contenir des balises <data> qui utilisent des attributs de balise de données existants, ainsi que les attributs android:query et android:fragment.
Voici un exemple de syntaxe AndroidManifest:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
Espace privé
L'espace privé permet aux utilisateurs de créer un espace distinct sur leur appareil afin de tenir leurs applications sensibles loin des regards indiscrets, protégées par un niveau d'authentification renforcé. L'espace privé utilise un profil utilisateur distinct. Pour verrouiller son espace privé, l'utilisateur peut choisir le verrouillage de l'écran ou une méthode différente.
Les applications de l'espace privé se trouvent dans un conteneur dédié dans le lanceur d'applications et n'apparaissent pas dans les vues récentes, les notifications, les paramètres, ni dans d'autres applications lorsque l'espace privé est verrouillé. Le contenu généré et téléchargé par l'utilisateur (comme les contenus multimédias ou les fichiers) sur l'espace privé et l'espace principal ainsi que les comptes de chacun de ces espaces sont distincts. La Sharesheet du système et le sélecteur de photos peuvent être utilisés pour autoriser les applications à accéder au contenu des différents espaces lorsque l'espace privé est déverrouillé.
Les utilisateurs ne peuvent pas déplacer les applications existantes et leurs données vers l'espace privé. À la place, les utilisateurs sélectionnent une option d'installation dans l'espace privé pour installer une application à l'aide de la plate-forme de téléchargement d'applications de leur choix. Les applications de l'espace privé sont installées en tant que copies distinctes de celles de l'espace principal (nouvelles copies de la même application).
Lorsqu'un utilisateur verrouille l'espace privé, le profil est arrêté. Lorsque le profil est arrêté, les applications de l'espace privé ne sont plus actives et ne peuvent pas effectuer d'activités de premier plan ni d'activités en arrière-plan, y compris afficher des notifications.
Nous vous recommandons de tester votre application avec un espace privé pour vous assurer qu'elle fonctionne comme prévu, en particulier si elle appartient à l'une des catégories suivantes:
- Applications avec une logique pour les profils professionnels qui supposent que toutes les copies installées de leur application qui ne se trouvent pas dans le profil principal se trouvent dans le profil professionnel.
- Applications médicales
- Applications de lanceur d'applications
- Applications de plate-forme de téléchargement d'applications
Interroger la dernière sélection d'utilisateur pour l'accès aux photos sélectionnées
Les applications ne peuvent désormais mettre en avant que les photos et vidéos sélectionnées le plus récemment lorsqu'un accès partiel aux autorisations multimédias est accordé. Cette fonctionnalité peut améliorer l'expérience utilisateur pour les applications qui demandent fréquemment l'accès aux photos et aux vidéos. Pour utiliser cette fonctionnalité dans votre application, activez l'argument QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY lorsque vous interrogez MediaStore via ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Privacy Sandbox sur Android
Android 15 inclut les dernières extensions Android Ad Services, qui intègrent la dernière version de la Privacy Sandbox sur Android. Cette addition s'inscrit dans notre travail visant à développer des technologies qui améliorent la confidentialité des utilisateurs et permettent de créer des expériences publicitaires efficaces et personnalisées pour les applications mobiles. Pour en savoir plus sur les programmes Preview développeur et bêta de la Privacy Sandbox sur Android, consultez notre page dédiée.
Santé Connect
Android 15 intègre les dernières extensions autour de Santé Connect par Android, une plate-forme sécurisée et centralisée permettant de gérer et de partager les données de santé et de remise en forme collectées par les applications. Cette mise à jour ajoute la prise en charge de types de données supplémentaires pour la forme physique, la nutrition, la température de la peau, les plans d'entraînement et plus encore.
Le suivi de la température cutanée permet aux utilisateurs de stocker et de partager des données de température plus précises à partir d'un accessoire connecté ou d'un autre appareil de suivi.
Les plans d'entraînement sont des plans d'entraînement structurés pour aider l'utilisateur à rester en forme objectifs. La prise en charge des plans de formation comprend plusieurs phases objectifs:
- Objectifs d'achèvement liés aux calories brûlées, à la distance parcourue, à la durée, aux répétitions et au nombre de pas.
- Objectifs de performance basés sur le nombre le plus élevé possible de répétitions (AMRAP), la cadence, la fréquence cardiaque, la puissance, l'intensité perçue et la vitesse.
Pour en savoir plus sur les dernières nouveautés de Santé Connect sur Android, consultez la présentation Créer des expériences adaptables avec Android Santé lors de Google I/O.
Partager le contenu d'une appli sur l'écran
Android 15 est compatible avec le partage d'écran d'application afin que les utilisateurs puissent partager ou enregistrer uniquement une fenêtre d'application plutôt que l'intégralité de l'écran de l'appareil. Cette fonctionnalité, activée pour la première fois dans Android 14 QPR2, inclut des appels de retour MediaProjection qui permettent à votre application de personnaliser l'expérience de partage d'écran de l'application. Notez que pour les applications ciblant Android 14 (niveau d'API 34) ou version ultérieure, l'autorisation de l'utilisateur est requise pour chaque session de capture MediaProjection.
Expérience utilisateur et UI du système
Android 15 offre aux développeurs d'applications et aux utilisateurs plus de contrôle et de flexibilité pour configurer leur appareil en fonction de leurs besoins.
Pour savoir comment utiliser les dernières améliorations d'Android 15 afin d'améliorer l'expérience utilisateur de votre application, consultez la conférence Améliorer l'expérience utilisateur de votre application Android de Google I/O.
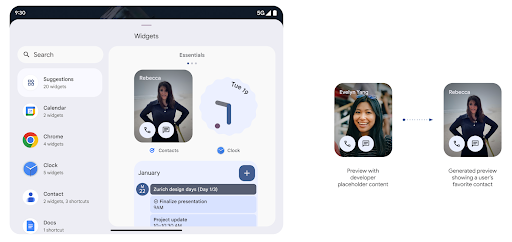
Aperçus de widgets plus riches avec l'API Generated Previews
Avant Android 15, le seul moyen de fournir des aperçus du sélecteur de widgets était de spécifier une ressource d'image ou de mise en page statique. Ces aperçus diffèrent souvent considérablement de l'apparence du widget réel lorsqu'il est placé sur l'écran d'accueil. De plus, les ressources statiques ne peuvent pas être créées avec Jetpack Glance. Un développeur Glance doit donc prendre une capture d'écran de son widget ou créer une mise en page XML pour obtenir un aperçu du widget.
Android 15 prend en charge les aperçus générés. Cela signifie que les fournisseurs de widgets d'application peuvent générer RemoteViews à utiliser comme aperçu du sélecteur au lieu d'une ressource statique.
API Push
Les applications peuvent fournir des aperçus générés via une API push. Les applications peuvent fournir des aperçus à tout moment de leur cycle de vie et ne reçoivent pas de demande explicite de la part de l'hôte. Les aperçus sont conservés dans AppWidgetService, et les hôtes peuvent les demander à la demande. L'exemple suivant charge une ressource de mise en page de widget XML et la définit en tant qu'aperçu:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
Le flux attendu est le suivant:
- Le fournisseur de widgets appelle
setWidgetPreviewà tout moment. Les aperçus fournis sont conservés dansAppWidgetServiceavec d'autres informations du fournisseur. setWidgetPreviewinforme les hôtes d'un aperçu mis à jour via le rappelAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged. En réponse, l'hôte du widget recharge toutes ses informations sur le fournisseur.- Lorsque l'hôte affiche un aperçu de widget, il vérifie
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories. Si la catégorie choisie est disponible, il appelleAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewpour renvoyer l'aperçu enregistré pour ce fournisseur.
Quand appeler le setWidgetPreview
Étant donné qu'il n'y a pas de rappel pour fournir des aperçus, les applications peuvent choisir d'envoyer des aperçus à tout moment lorsqu'elles s'exécutent. La fréquence d'actualisation de l'aperçu dépend du cas d'utilisation du widget.
La liste suivante décrit les deux principales catégories de cas d'utilisation d'aperçu:
- Fournisseurs qui affichent des données réelles dans leurs aperçus de widgets, comme des informations personnalisées ou récentes. Ces fournisseurs peuvent définir l'aperçu une fois que l'utilisateur s'est connecté ou a effectué la configuration initiale dans son application. Ensuite, ils peuvent configurer une tâche périodique pour mettre à jour les aperçus à la fréquence de leur choix. Il peut s'agir d'un widget photo, d'un widget agenda, d'un widget météo ou d'un widget d'actualités.
- Fournisseurs qui affichent des informations statiques dans des aperçus ou des widgets d'action rapide qui n'affichent aucune donnée. Ces fournisseurs peuvent définir des aperçus une seule fois, lors du premier lancement de l'application. Exemples de ce type de widget : widget d'actions rapides Drive ou widget de raccourcis Chrome.
Certains fournisseurs peuvent afficher des aperçus statiques dans le sélecteur de mode Hub, mais des informations réelles dans le sélecteur de l'écran d'accueil. Ces fournisseurs doivent suivre les consignes pour ces deux cas d'utilisation afin de définir des aperçus.
Picture-in-picture
Android 15 introduit des modifications en mode Picture-in-picture (PIP) pour garantir une transition plus fluide en mode PIP. Cela sera bénéfique pour des applications avec des éléments d'interface utilisateur superposés à leur interface utilisateur principale, qui va dans le mode PIP.
Les développeurs utilisent le rappel onPictureInPictureModeChanged pour définir une logique qui active/désactive la visibilité des éléments d'interface utilisateur superposés. Ce rappel est
déclenché lorsque l'animation d'entrée ou de sortie du mode PIP est terminée. À partir d'Android 15, la classe PictureInPictureUiState inclut un autre état.
Avec cet état d'interface utilisateur, les applications ciblant Android 15 (niveau d'API 35) observeront le rappel Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged appelé avec isTransitioningToPip() dès le début de l'animation PIP. Il y a
de nombreux éléments d'interface utilisateur qui ne sont pas pertinents pour l'application en mode PIP, par
des exemples de vues ou de mise en page incluant des informations telles que des suggestions,
les vidéos, les avis et les titres. Lorsque l'application passe en mode PIP, utilisez la
Rappel onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged pour masquer ces éléments d'interface utilisateur. Lorsque
passe en mode plein écran depuis la fenêtre PIP, utilisez
onPictureInPictureModeChanged pour afficher ces éléments, comme indiqué dans
les exemples suivants:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
Cette option d'activation/de désactivation rapide de la visibilité des éléments d'interface utilisateur non pertinents (pour une fenêtre PiP) permet d'assurer une animation d'entrée PiP plus fluide et sans scintillement.
Règles "Ne pas déranger" améliorées
AutomaticZenRule permet aux applications de personnaliser la fonctionnalité Attention
Règles de gestion (Ne pas déranger) et décidez quand l'activer ou le désactiver
de l'IA générative. Android 15 améliore considérablement ces règles dans le but d'améliorer
l'expérience utilisateur. Les améliorations suivantes sont incluses:
- Ajout de types à
AutomaticZenRule, ce qui permet au système d'appliquer un traitement spécial à certaines règles. - Ajout d'une icône à
AutomaticZenRulepour rendre les modes plus reconnaissables. - Ajouter une chaîne
triggerDescriptionàAutomaticZenRulequi décrit les conditions selon lesquelles la règle doit être activée pour l'utilisateur. - Ajoutée(s)
ZenDeviceEffectsàAutomaticZenRule, ce qui permet aux règles de déclencher, par exemple, des niveaux de gris l'affichage, le mode Nuit ou la diminution de la luminosité du fond d'écran.
Définir VibrationEffect pour les canaux de notification
Android 15 permet de définir des vibrations riches pour les notifications entrantes par canal à l'aide de NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect. Vos utilisateurs peuvent ainsi distinguer les différents types de notifications sans avoir à regarder leur appareil.
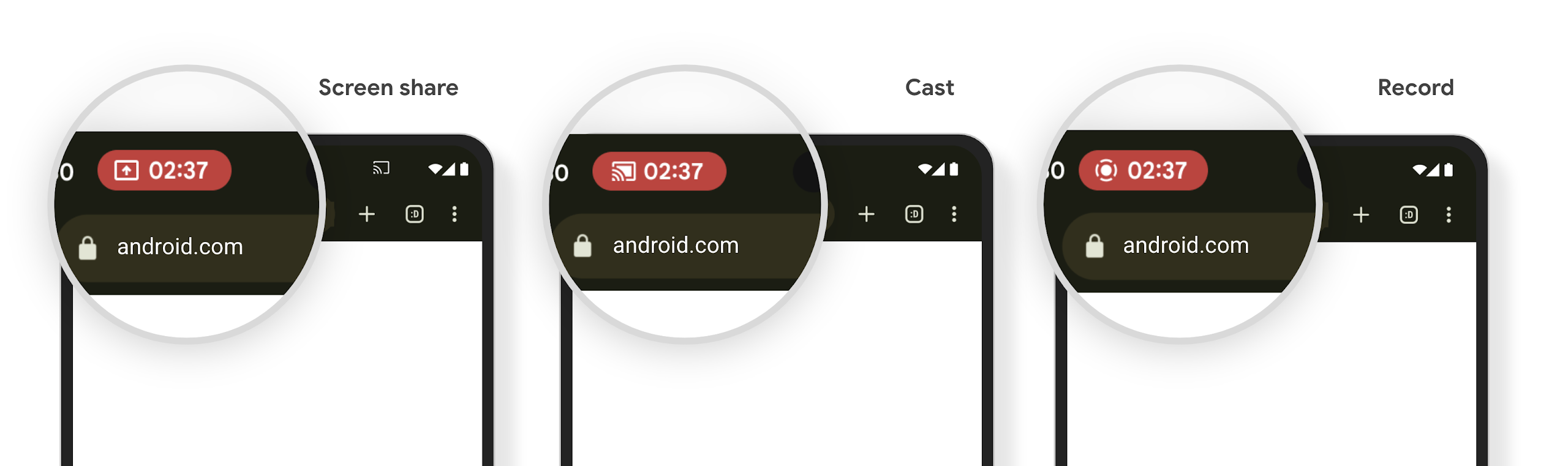
Chip de la barre d'état de la projection multimédia et arrêt automatique
La projection multimédia peut exposer des informations personnelles des utilisateurs. Un nouveau chip de barre d'état proéminent informe les utilisateurs de toute projection d'écran en cours. Les utilisateurs peuvent appuyer sur le chip pour arrêter la diffusion, le partage ou l'enregistrement de l'écran. De plus, pour une expérience utilisateur plus intuitive, toute projection d'écran en cours s'arrête désormais automatiquement lorsque l'écran de l'appareil est verrouillé.
Grands écrans et facteurs de forme
Android 15 permet à vos applications de tirer le meilleur parti des facteurs de forme d'Android, y compris les grands écrans, les appareils à clapet et les pliables.
Amélioration du multitâche sur grand écran
Android 15 offre aux utilisateurs de meilleurs moyens d'effectuer plusieurs tâches en même temps sur les appareils à grand écran. Pour Par exemple, les utilisateurs peuvent enregistrer leurs combinaisons d'applications en écran partagé préférées pour des accéder à la barre des tâches et l'épingler à l'écran pour passer rapidement d'une application à l'autre. Il est donc plus important que jamais de vous assurer que votre application est adaptative.
Google I/O propose des sessions sur la création d'applications Android adaptatives applications et Créer une interface utilisateur avec Material 3 bibliothèque adaptative et notre documentation peut vous aider. Concevoir pour les grands écrans.
Compatibilité avec l'écran de couverture
Votre application peut déclarer une propriété qu'Android 15 utilise pour permettre à votre Application ou Activity d'être présenté sur les petits écrans de couverture des appareils à clapet compatibles. Ces écrans sont trop petits pour être considérés comme des cibles compatibles pour les applications Android, mais votre application peut les prendre en charge, ce qui la rend disponible dans plus d'endroits.
Connectivité
Android 15 met à jour la plate-forme pour permettre à votre application d'accéder aux dernières avancées en matière de technologies de communication et sans fil.
Assistance par satellite
Android 15 continue d'étendre la prise en charge de la plate-forme pour la connectivité par satellite et inclut certains éléments d'interface utilisateur pour garantir une expérience utilisateur cohérente sur l'ensemble des de la connectivité par satellite.
Les applications peuvent utiliser ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() pour :
détecter lorsqu'un appareil est connecté à un satellite, ce qui leur permet de mieux connaître
pourquoi les services réseau
complètes peuvent être indisponibles. De plus, Android 15
prend en charge les applications de SMS et MMS, ainsi que les applications RCS préchargées à utiliser.
la connectivité satellite pour
envoyer et recevoir des messages.

Expériences NFC plus fluides
Android 15 vise à rendre l'expérience de paiement sans contact plus fluide et fiable, tout en continuant à prendre en charge l'écosystème d'applications NFC robuste d'Android. Sur les appareils compatibles, les applications peuvent demander à NfcAdapter de passer en mode observation, où l'appareil écoute, mais ne répond pas aux lecteurs NFC, en envoyant les objets PollingFrame du service NFC de l'application à traiter. Les objets PollingFrame peuvent être utilisés pour l'authentification avant la première communication avec le lecteur NFC, ce qui permet une transaction en un seul geste dans de nombreux cas.
De plus, les applications peuvent enregistrer un filtre sur les appareils compatibles afin d'être informées de l'activité de la boucle de sondage, ce qui permet un fonctionnement fluide avec plusieurs applications compatibles avec la technologie NFC.
Rôle Wallet
Android 15 introduit un rôle Wallet qui permet une intégration plus étroite avec l'application de portefeuille préférée de l'utilisateur. Ce rôle remplace le paramètre de paiement sans contact par défaut du NFC. Les utilisateurs peuvent gérer le titulaire du rôle Wallet en accédant à Paramètres > Applications > Applications par défaut.
Le rôle Wallet est utilisé lors du routage des pressions NFC pour les AID enregistrés dans la catégorie de paiement. Les pressions sont toujours dirigées vers le titulaire du rôle Wallet, sauf si une autre application enregistrée pour le même AID s'exécute au premier plan.
Ce rôle permet également de déterminer l'emplacement du bloc d'accès rapide Wallet lorsqu'il est activé. Lorsque le rôle est défini sur "Aucun", la carte d'accès rapide n'est pas disponible et les paiements par contact NFC ne sont envoyés qu'à l'application au premier plan.
Sécurité
Android 15 vous aide à renforcer la sécurité de votre application, à protéger ses données et à offrir aux utilisateurs plus de transparence et de contrôle sur leurs données. Pour en savoir plus sur ce que nous faisons pour améliorer la protection des utilisateurs et protéger votre application contre les nouvelles menaces, consultez la conférence Safeguarding user security on Android de Google I/O.
Intégrer Credential Manager à la saisie automatique
À partir d'Android 15, les développeurs peuvent associer des vues spécifiques telles que les champs de nom d'utilisateur ou de mot de passe à des requêtes du Gestionnaire d'identifiants, ce qui facilite la fourniture d'une expérience utilisateur personnalisée lors du processus de connexion. Lorsque l'utilisateur met en surbrillance l'une de ces vues, une requête correspondante est envoyée au Gestionnaire d'identifiants. Les identifiants obtenus sont agrégés entre les fournisseurs et affichés dans les UI de remplacement de la saisie automatique, telles que les suggestions intégrées ou les suggestions déroulantes. La bibliothèque Jetpack androidx.credentials est le point de terminaison recommandé pour les développeurs. Elle sera bientôt disponible pour améliorer davantage cette fonctionnalité dans Android 15 et versions ultérieures.
intégrer l'inscription et la connexion en un seul geste aux invites biométriques ;
Le Gestionnaire d'identifiants intègre les invites biométriques aux processus de création et de connexion des identifiants, ce qui évite aux fournisseurs de gérer les invites biométriques. Par conséquent, les fournisseurs d'identifiants n'ont qu'à se concentrer sur les résultats des flux de création et d'obtention, complétés par le résultat du flux biométrique. Ce processus simplifié crée des identifiants plus efficaces et simplifiés. de création et de récupération.
Gestion des clés pour le chiffrement de bout en bout
Nous lançons E2eeContactKeysManager dans Android 15, qui facilite le chiffrement de bout en bout dans vos applications Android en fournissant une API au niveau de l'OS pour le stockage des clés publiques cryptographiques.
E2eeContactKeysManager est conçu pour s'intégrer à l'application de contacts de la plate-forme afin de permettre aux utilisateurs de gérer et de valider de manière centralisée les clés publiques de leurs contacts.
Vérification des autorisations sur les URI de contenu
Android 15 introduit un ensemble d'API qui effectuent des vérifications d'autorisation sur les URI de contenu:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: effectue une vérification complète des autorisations sur les URI de contenu.- Attribut de fichier manifeste
ActivityrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: applique les autorisations spécifiées aux URI de contenu fournis au lancement de l'activité. - Classe
ComponentCallerpour les appelantsActivity: représente l'application qui a lancé l'activité.
Accessibilité
Android 15 ajoute des fonctionnalités qui améliorent l'accessibilité pour les utilisateurs.
Better Braille
Dans Android 15, TalkBack est compatible avec les écrans braille qui utilisent la norme HID via USB et Bluetooth sécurisé.
Cette norme, semblable à celle utilisée par les souris et les claviers, aidera Android à prendre en charge un plus grand nombre de plages braille au fil du temps.
Internationalisation
Android 15 ajoute des fonctionnalités qui complètent l'expérience utilisateur lorsqu'un appareil est utilisé dans différentes langues.
Police variable CJK
À partir d'Android 15, le fichier de police pour les langues chinoise, japonaise et coréenne (CJK), NotoSansCJK, est désormais une police variable. Les polices variables offrent de nouvelles possibilités de typographie créative dans les langues CJK. Les concepteurs peuvent explorer une gamme plus large de styles et créer des mises en page visuellement frappantes qui étaient auparavant difficiles ou impossibles à réaliser.

Justification entre les caractères
À partir d'Android 15, le texte peut être justifié en utilisant l'espacement entre les lettres
à l'aide de JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. La justification entre les mots a été introduite pour la première fois dans Android 8.0 (niveau d'API 26). La justification entre les caractères offre des fonctionnalités similaires pour les langues qui utilisent le caractère d'espacement pour la segmentation, comme le chinois, le japonais et d'autres.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.Configuration des retours à la ligne automatiques
Android a commencé à accepter les sauts de ligne basés sur les expressions pour le japonais et le coréen dans
Android 13 (niveau d'API 33). Toutefois, bien que les sauts de ligne basés sur des phrases améliorent la lisibilité des lignes courtes, ils ne fonctionnent pas bien pour les lignes longues.
Sous Android 15, les applications ne peuvent appliquer des sauts de ligne basés sur des expressions que pour les lignes courtes
de texte, à l'aide de la méthode LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
. Cette option permet de sélectionner la meilleure option de style de mot pour le texte.
Pour les lignes de texte courtes, des sauts de ligne en fonction d'une expression sont utilisés,
en tant que LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, comme indiqué dans
image suivante:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applique des sauts de ligne en fonction des expressions pour améliorer la lisibilité du texte.
Cela revient à appliquer
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASEPour les lignes de texte plus longues, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO utilise un "no"
saut de ligne, qui fonctionne de la même manière que
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, comme indiqué dans les
image suivante:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO n'applique aucun style de mot avec saut de ligne pour améliorer la lisibilité du texte.
Cela revient à appliquer LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.Police Hentaigana japonaise supplémentaire
Dans Android 15, un fichier de police pour l'ancien hiragana japonais (appelé Hentaigana) est regroupé par défaut. Les formes uniques des personnages Hentaigana permettent d'ajouter à l'œuvre ou au design, tout en préservant la précision transmission et compréhension des anciens documents japonais.

Cône VideoLAN Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. Ce logo ou une version modifiée peut être utilisé ou modifié par n'importe qui pour faire référence au projet VideoLAN ou à tout produit développé par l'équipe VideoLAN, mais n'indique pas l'approbation du projet.
Vulkan et le logo Vulkan sont des marques déposées de The Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL est une marque déposée, et le logo OpenGL ES est une marque de Hewlett Packard Enterprise utilisée avec autorisation par Khronos.
